A Hybrid Hydrophobic-Hydrophilic Coating with Combined Anti-Reflective and Anti-Soiling Properties
As a DuraMAT project, the College of Staten Island (CSI) is developing a novel and low-cost hybrid hydrophobic-hydrophilic coating for photovoltaic (PV) modules. The coating combines excellent anti-reflective and anti-soiling properties with abrasion resistance based on a patent-pending, lamentation-peeling technology.
The coating reduces reflections by >75% because of the low index of refraction and the morphology of the coating. Typically, reflections from the outer glass surface of PV panels results in losses of over 4%; losses from soiling are greater and may reach up to 50% of the energy produced.
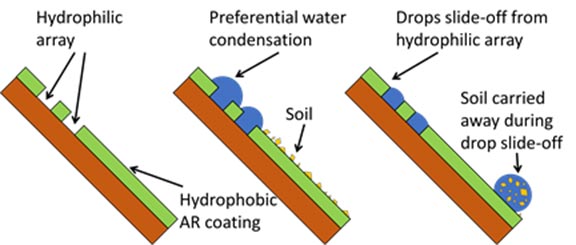
Anti-soiling properties are achieved using a combination of mechanisms: preferential nucleation and growth of liquid water droplets on hydrophilic regions during natural condensation (i.e., dew) and high droplet mobility on the hydrophobic surface.
Once droplets reach a critical mass, they slide off, imbibing and carrying away soil that has been deposited on the surface. CSI is benchmarking the durability and reliability using standard PV test conditions. Anti-soiling properties are being assessed in outdoor field trials and laboratory soiling studies.
Realizing these properties would achieve up to 91% of the SunShot 2030 O&M cost-reduction goal of 0.7¢/kWh.
Core Objective
Location
CSI of the City University of New York and National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Applications
Hybrid hydrophobic-hydrophilic coatings can be applied to any type of glass, including low-iron solar cover glass, to reduce reflection and decrease the accumulation of soil on surfaces. This includes architectural windows, solar PV modules, and mirrors for concentrated solar power.
Availability
It's available to NREL scientists and external collaborators.
References
Nayshevsky, I.; Xu, Q.; Lyons, A. (2018). “Hydrophobic-Hydrophilic Surfaces Exhibiting Dropwise Condensation for Anti-Soiling Applications.” 2018 IEEE 45th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference.
Nayshevsky, I.; Xu, Q.; Barahman, G.; Lyons, A. (2017). “Self-Cleaning Effects of the Anti-Soiling and Anti-Reflective Textured Fluoropolymer Nano coatings.” 2017 IEEE 44rd Photovoltaic Specialists Conference.
Mondal, B.; Eain, M.M.G.; Xu, Q.; Egan, V.M.; Punch, J.; Lyons, A.M. (2015). “Design and Fabrication of a Hybrid Superhydrophobic–Hydrophilic Surface That Exhibits Stable Dropwise Condensation.” ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, vol. 7, no. 42, pp. 23575–23588.
Contact
To learn more about this project, contact Alan Lyons.